The Khanna Vision Institute’s advanced diagnostic tools, such as topography, pachymetry mapping, and Pentacam, provide a comprehensive understanding of the cornea’s intricate structure. Topography, a detailed map of the corneal surface, reveals the unique curvature and irregularities that can impact vision. Pachymetry, a precise measurement of corneal thickness, is essential for identifying potential issues like corneal thinning or irregularities. The Pentacam, a state-of-the-art imaging system, offers a 3D analysis of the cornea, providing valuable insights into its shape, thickness, and overall health. These cutting-edge technologies, combined with the expertise of the Khanna Vision Institute’s team, enable a thorough assessment of each patient’s corneal characteristics, allowing for personalized treatment plans and optimal visual outcomes. By leveraging these advanced diagnostic tools, the Khanna Vision Institute ensures that patients receive the most accurate and tailored care, empowering them to achieve their desired vision goals.
Corneal Topography
Purpose:
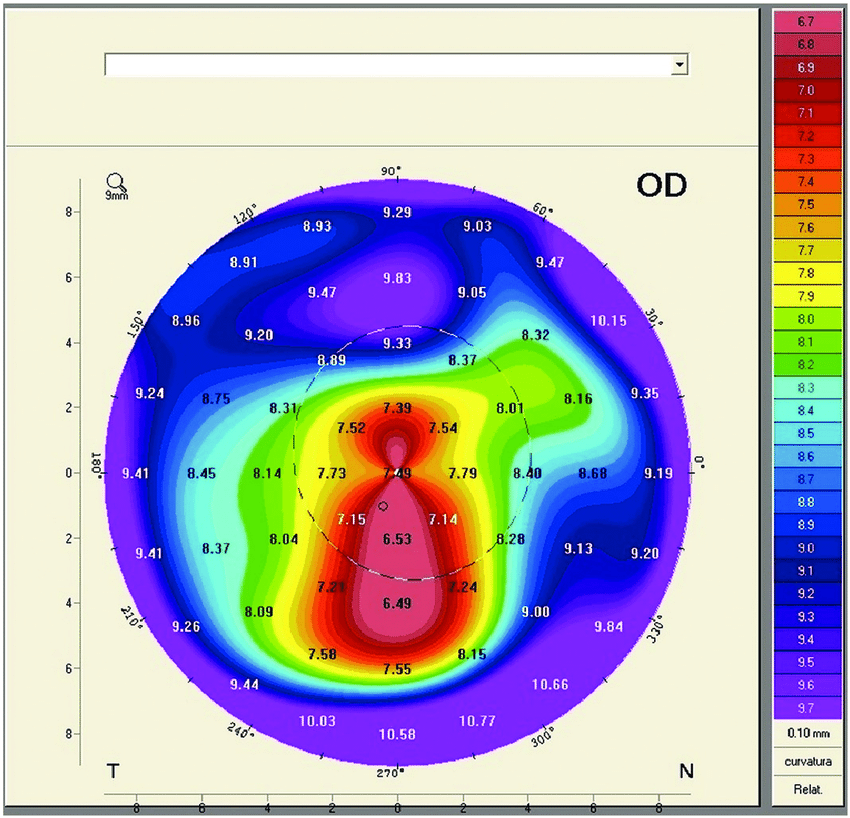
Corneal topography provides a detailed map of the corneal surface curvature. It is critical for diagnosing and monitoring keratoconus.
Procedure:
The patient places their head on a chin rest, and the topographer projects rings of light onto the cornea.
The device captures reflected light and generates a color-coded map of the corneal surface.
Key Features in Keratoconus:
Asymmetry: Significant irregularity and asymmetry in the corneal shape.
Steepening: Localized steepening, often in the inferior or central cornea, indicating the cone.
Inferior-Superior (I-S) Ratio: A higher I-S ratio suggests keratoconus.
Keratometric Readings: High keratometric values (K-values) indicating increased curvature.
Pachymetry Map
Purpose:
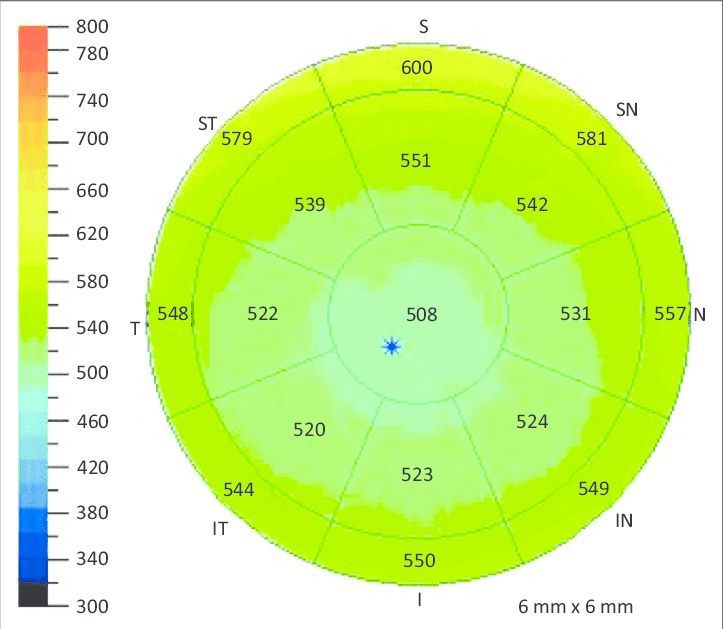
Pachymetry measures the corneal thickness at various points. It is crucial for assessing corneal thinning in keratoconus.
Procedure:
Similar to topography, the patient looks into a device that uses ultrasound or optical coherence to measure corneal thickness.
A detailed map showing thickness variations across the cornea is produced.
Key Features in Keratoconus:
Thinning: Localized thinning in the central/paracentral cornea.
Thinnest Location: Identifying the thinnest point, which is often displaced inferiorly in the keratoconus.
Thickness Gradient: A steep gradient of thickness from the center to the periphery.
Pentacam
Purpose:
The Pentacam (a type of Scheimpflug camera) provides a comprehensive 3D analysis of the anterior segment of the eye, including corneal topography, pachymetry, and anterior and posterior corneal surfaces.
Procedure:
The patient places their head on a chin rest, and the Pentacam captures images of the cornea from multiple angles.
The device generates a 3D model and detailed maps of the cornea.
Key Features in Keratoconus:
Anterior and Posterior Elevation Maps: Shows elevations relative to a best-fit sphere, highlighting protrusions on both corneal surfaces.
Belin/Ambrosio Enhanced Ectasia Display: Combines anterior and posterior curvature and pachymetric data to enhance sensitivity in detecting early keratoconus.
Corneal Thickness Spatial Profile (CTSP): Evaluates the distribution of corneal thickness across different regions.
Corneal Asphericity (Q-value): Measures the shape of the cornea, with abnormal values indicating keratoconus.
Diagnostic Criteria for Keratoconus
Early Keratoconus:
Mild asymmetry and localized steepening on topography.
Slight thinning on the pachymetry map.
Subtle changes in the anterior and the posterior elevation on Pentacam.
Moderate Keratoconus:
More pronounced steepening and irregularity on topography.
Significant thinning and displacement of the thinnest point on the pachymetry map.
Clear elevation changes on both anterior and posterior surfaces on Pentacam.
Advanced Keratoconus:
Severe irregularity and steepening on topography.
Marked thinning, often with scarring on the pachymetry map.
Major elevation changes and possible corneal opacities on Pentacam.
Advantages of Using These Tools
Early Detection: Identifies keratoconus before significant visual symptoms develop.
Detailed Mapping: Provides comprehensive data on corneal shape and thickness.
Monitoring Progression: Tracks changes over time to assess disease progression.
Treatment Planning: Helps in planning interventions like corneal cross-linking, intracorneal ring segments, or keratoplasty.